What is the Internet?
The Internet is a vast network of interconnected computers that allows people worldwide to share information, communicate, and perform various activities online. It operates using standardized communication protocols, such as TCP/IP, enabling devices to exchange data seamlessly.
This network connects billions of devices, including computers, smartphones, and IoT gadgets, forming the backbone of modern digital life.
From browsing websites to streaming videos and shopping online, the Internet plays an essential role in our personal and professional lives.
Table of Contents
History of the Internet
The Internet’s history dates back to the 1960s with the creation of ARPANET (Advanced Research Projects Agency Network), developed by the U.S. Department of Defense. ARPANET aimed to establish a decentralized communication network that could survive potential disruptions.
Key milestones in Internet history include:
- 1969: The first message was sent over ARPANET.
- 1983: TCP/IP protocols were adopted, standardizing data communication.
- 1989: Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web, a system of hyperlinked documents accessible via the Internet.
- 1991: The first website went live, making the Internet accessible to the public.
Today, the Internet has transformed into a global platform connecting over 5 billion users.
How the Internet Works
At its core, the Internet operates by transferring data packets between devices using protocols like TCP/IP. Here’s a simplified explanation of how it works:
- Servers and Clients: Servers store information, while clients (e.g., your browser) request it.
- DNS (Domain Name System): Converts human-readable URLs like “www.example.com” into IP addresses, allowing devices to locate and connect with servers.
- Data Transfer: Data is broken into packets, sent over the network, and reassembled at the destination.
This seamless exchange of data enables activities like browsing, streaming, and online communication.
Uses of the Internet
The Internet is an indispensable tool that has revolutionized various aspects of our lives:
- Communication: Enables instant communication via emails, social media, and video calls.
- Information Access: Provides endless resources for learning, research, and news.
- E-Commerce: Facilitates online shopping, digital payments, and business transactions.
- Entertainment: Offers streaming platforms, gaming, and social media for leisure.
- Education: Supports e-learning platforms, virtual classrooms, and online courses.
The versatility of the Internet makes it an essential resource for individuals, businesses, and organizations.
Impact of the Internet on Society
The Internet has brought significant changes to how we live and work:
Positive Impacts:
- Global Connectivity: Brings people closer through social media and communication tools.
- Economic Growth: Supports businesses, e-commerce, and job creation.
- Access to Information: Democratizes knowledge and fosters innovation.
Challenges:
- Cybersecurity Risks: Increased threats of hacking and data breaches.
- Digital Divide: Unequal access to the Internet in developing regions.
- Misinformation: Spread of fake news and unreliable content.
Addressing these challenges is crucial to maximizing the benefits of the Internet.
Technologies Behind the Internet
The Internet relies on a combination of hardware and software to function:
- Hardware: Includes routers, modems, servers, and cables that facilitate connectivity.
- Software: Web browsers, email clients, and development tools that enable users to interact with the Internet.
Emerging technologies like 5G, cloud computing, and the Internet of Things (IoT) are shaping the Internet’s future by making it faster, more reliable, and more integrated into daily life.
Internet Accessibility
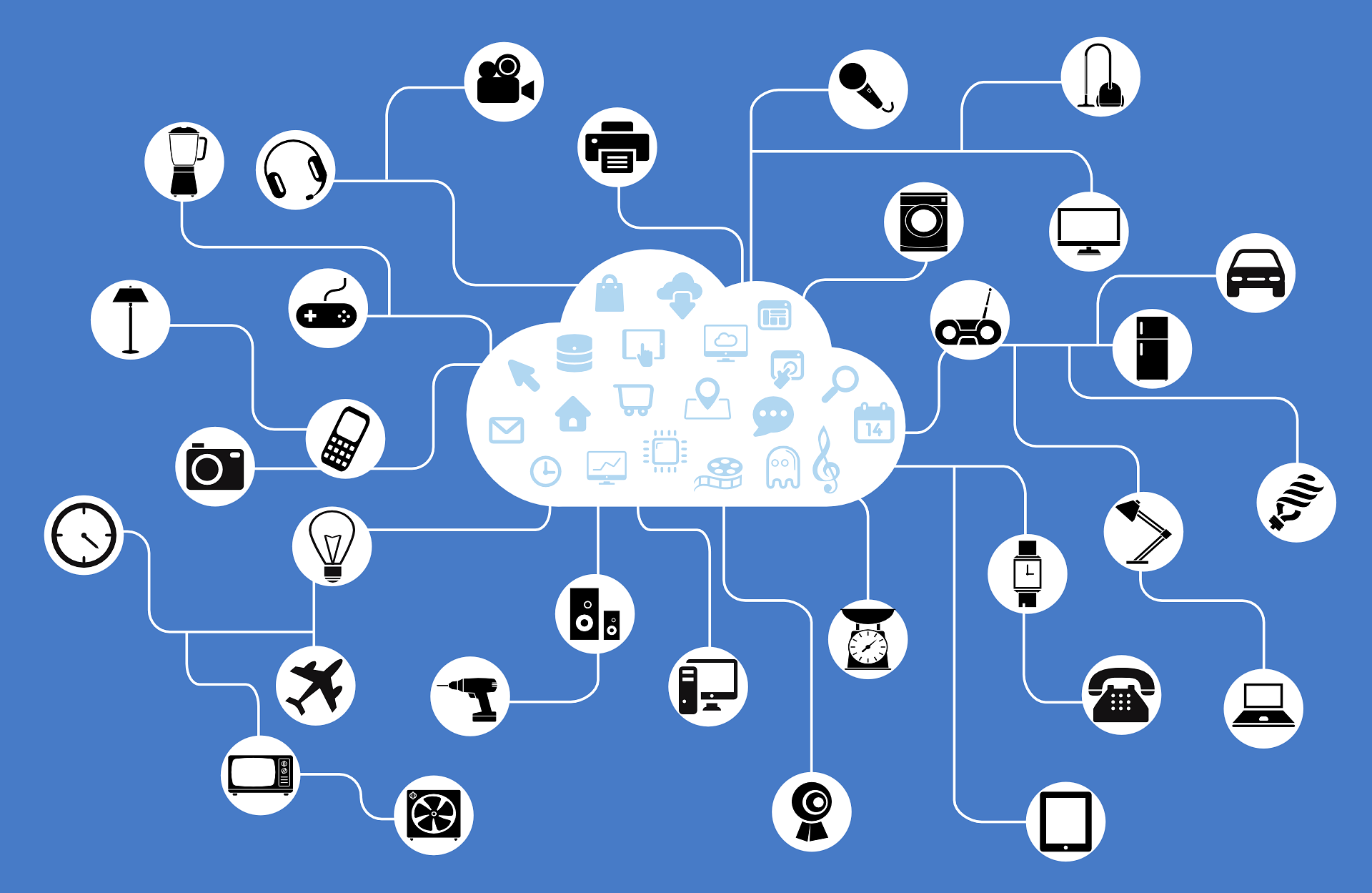
The Internet is accessed through wired connections (fiber, DSL) or wireless technologies (Wi-Fi, mobile data). Despite its widespread use, millions of people still lack access due to infrastructure or economic challenges.
Global initiatives like satellite Internet projects (e.g., Starlink) aim to bridge this digital divide and bring Internet connectivity to remote and underserved regions.
Safety and Security on the Internet
Staying safe online is a priority in today’s interconnected world. Key tips include:

- Use strong, unique passwords for your accounts.
- Be cautious of phishing emails and suspicious links.
- Enable two-factor authentication for added security.
- Regularly update software and use antivirus tools.
Encryption, firewalls, and VPNs also play a vital role in protecting sensitive information.
Future of the Internet
The Internet is continuously evolving, with advancements like:
- Web 3.0: A decentralized Internet powered by blockchain technology.
- AI and Machine Learning: Enhancing personalization and automating tasks.
- Quantum Computing: Promising unprecedented processing speeds.
These innovations will redefine how we interact with technology, creating a smarter and more efficient Internet.
Fun Facts About the Internet
- The first email was sent in 1971 by Ray Tomlinson.
- Over 5 billion people use the Internet as of 2024.
- The Internet weighs about the same as a strawberry (in terms of the energy required to keep it running).
- The first search engine, “Archie,” was created in 1990.
- More than 1.8 billion websites exist today, but not all are active.
Conclusion
The Internet is the backbone of modern life, transforming communication, business, and education. Its history, workings, and uses highlight its significance in our daily lives. While it presents challenges like cybersecurity and the digital divide, its potential for innovation and global connectivity is unparalleled.
By understanding its fundamentals, we can use the Internet responsibly and harness its power to shape a better future click here to read more such blogs.
FAQs : Introduction to the Internet
1. What is the Internet in simple terms?
The Internet is a global network of computers that allows people to share information and communicate.
2. Who invented the Internet?
The Internet was developed through various contributions, but ARPANET, funded by the U.S. Department of Defense, is considered its precursor. Tim Berners-Lee invented the World Wide Web, which made the Internet accessible to the public.
3. How is the Internet different from the World Wide Web?
The Internet is the infrastructure that connects devices globally, while the World Wide Web is a system of interconnected documents and multimedia accessible via the Internet.
4. What are the major uses of the Internet?
The Internet is used for communication, information sharing, online shopping, entertainment, education, and business transactions.
5. What does the future of the Internet look like?
The future of the Internet includes advancements in Web 3.0, AI, quantum computing, and global connectivity, promising faster and smarter digital experiences.

